Research Projects
This page highlights some of my past and current projects, organized by areas. For detailed descriptions and related publications, click the thumbnail or the "more info" link in each entry.
For a complete list of my publications, see my Google Scholar page.
Transferability estimation in transfer learning
Learning Optimal Prompt Ensemble for Multi-source Visual Prompt Transfer (AAAI’26)
A dynamic prompt ensemble framework that learns optimal weights over multiple pre-trained source prompts for a target task by jointly maximizing prompt transferability and minimizing gradient conflicts. (more info)
Exploiting Task Relationships in Continual Learning via Transferability-Aware Task Embeddings (NeurIPS 2025)
A rehearsal-free continual learning framework that leverages inter-task relationships through transferability-aware task embeddings. The proposed framework enhances both forward and backward transfer with low memory cost across diverse backbones. (more info)
A High-Dimensional Statistical Method for Optimizing Transfer Quantities in Multi-Source Transfer Learning (NeurIPS 2025)
A theoretical framework for determining the optimal quantity of source samples needed from each source task to jointly train the target model. This approach improves training efficiency, reduces data cost, and offers an intuitive understanding of the bias-variance tradeoff in multi-source transfer learning. (more info)
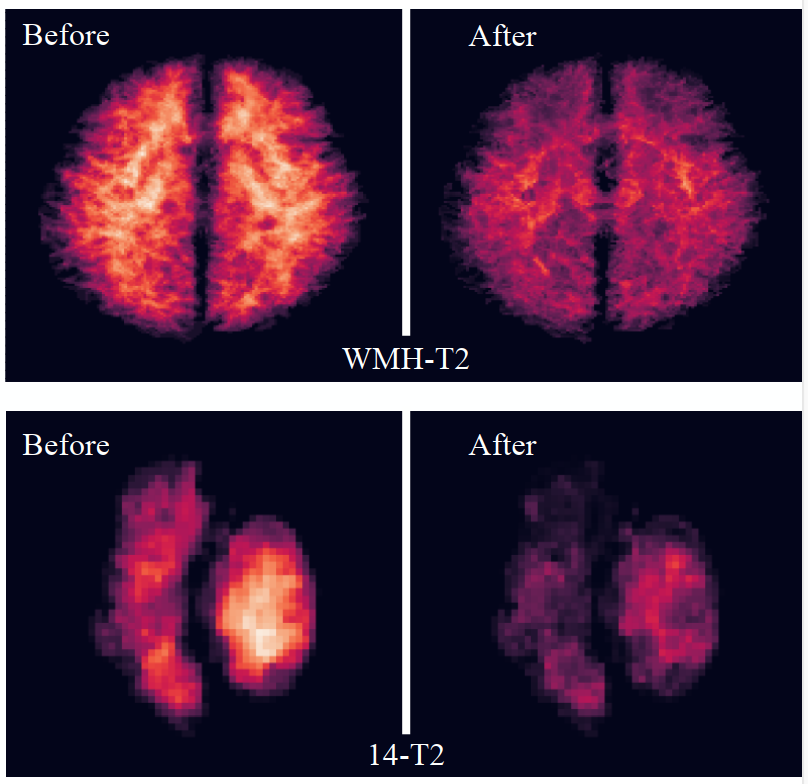
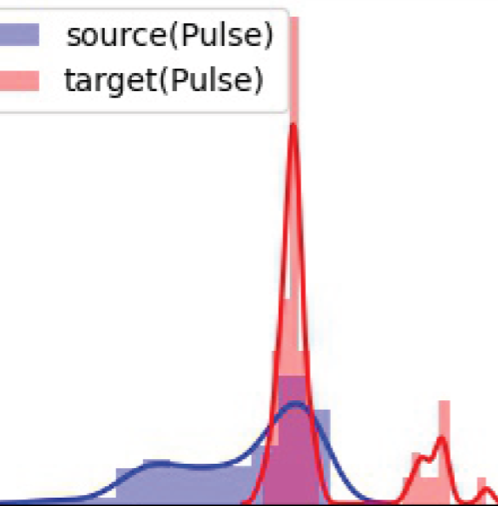
Transfer Risk Map: Mitigating Pixel-level Negative Transfer in Medical Segmentation. (ICASSP’24)
How to mitigate negative transfer in transfer learning is a long-standing challenge, especially in medical image segmentation. We propose a simple yet effective weighted fine-tuning method that directs the model's attention towards regions with significant transfer risk, measured based on pixel-wise transferability. (more info)
Transferability-Guided Cross-Domain Cross-Task Transfer Learning (IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2024)
We propose two new transferability metrics for cross-domain cross-task transfer learning. They signifcantly improve upon previous methods in computation efficiency and accuracy, and can serve as an objective function to enhance downstream transfer learning tasks. (more info)
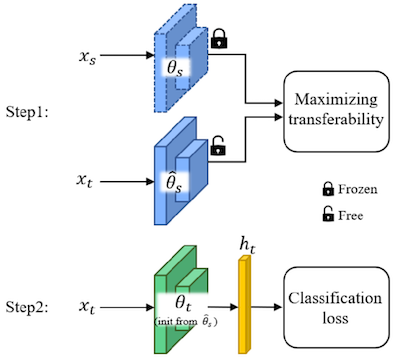
H-ensemble: An Information Theoretic Approach to Reliable Few-Shot Multi-Source-Free Transfer (AAAI’24)
A framework that learns an optimal linear combination of pre-trained source models (a.k.a. source ensemble) to a given target task by maximizing transferability. Leading to a multi-source transfer learning model that does not reply on having source model details or source training data. (more info)
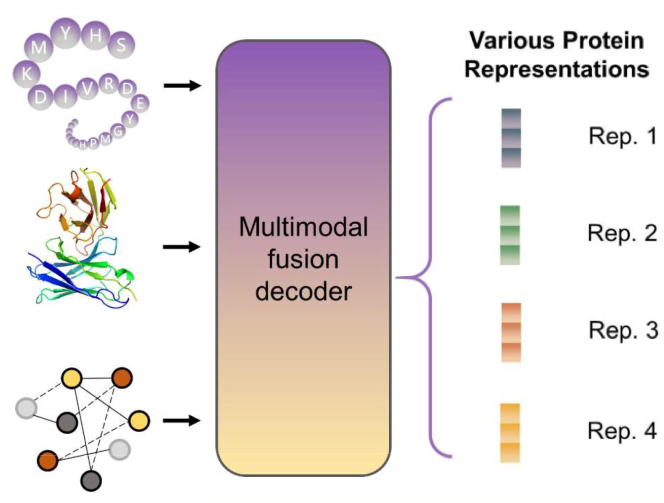
A Transferability-Based Method for Evaluating the Protein Representation Learning (IEEE J. of Bio and Health Inform., 2024)
A quantitative approach to estimate the performance of transferring pre-trained protein representations to downstream tasks. Unlike previous transferability metric designed for single-task representations, this method is designed to work with multi-task pretrained models. (more info)
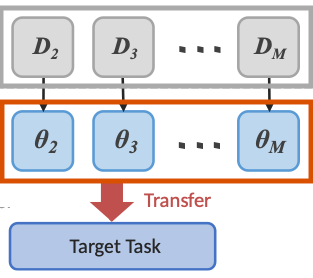
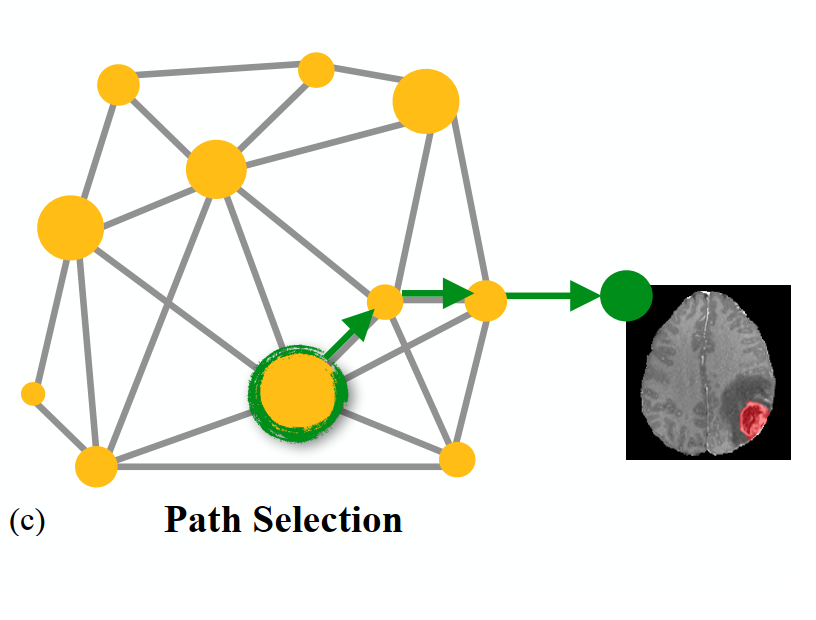
Graph-guided Sequential Transfer for Medical Image Segmentation. (IEEE BIBM’24)
A graph-based source selection framework for enhancing sequential transfer learning for medical image segmentation. Given a target task, it identifies the landmark source tasks and finds an effective sequential transfer path that gives the best target performance. (more info)
Efficient Prediction of Model Transferability in Semantic Segmentation Tasks. (ICIP’23)
Efficiently adapts transferability metrics for semantic segmentation. Based on the adapted metric, an transferability-weighted fine-tuning approach for transfering between semantic segmentation tasks is proposed. (more info)
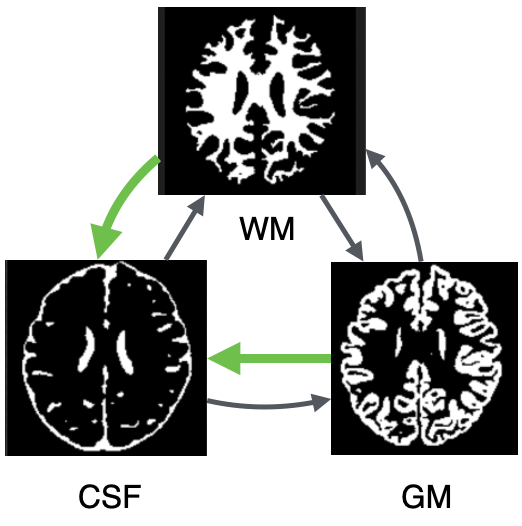
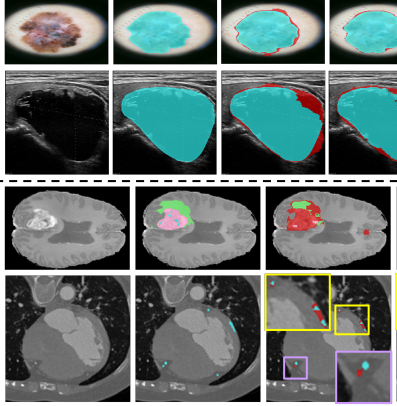
Finding the most transferable task for MRI brain segmentation. (BIBM’22)
A knowledge and transferability-based source task selection framework for the transfer learning among MRI brain segmentation tasks. Empirical studies reveals that modality information and segmentation mask structural similarity can significantly improve the transferability estimation between different segmentation tasks. (more info)
OTCE: A transferability metric for cross-domain cross-task representations. (CVPR’21)
A new transferability metric is presented for transfer learning across heterogeneous data distributions (a.k.a. domains) and distinct tasks. It characterizes transferability as a combination of domain difference and task difference and explicitly evaluates them from data in a unified framework. (more info)
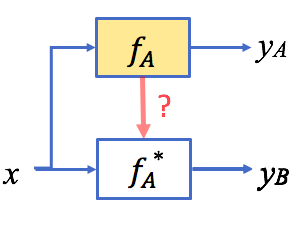
An information-theoretic metric to transferability for task transfer learning (IEEE ICIP’19)
Given a common input domain, a transferability metric estimates to what extent knowledge from a source task can help in learning a target task. We present a novel metric, rooted in information theory and statistics, to efficiently compute task transferability between classification problems. (more info)
Domain adaptation & generalization
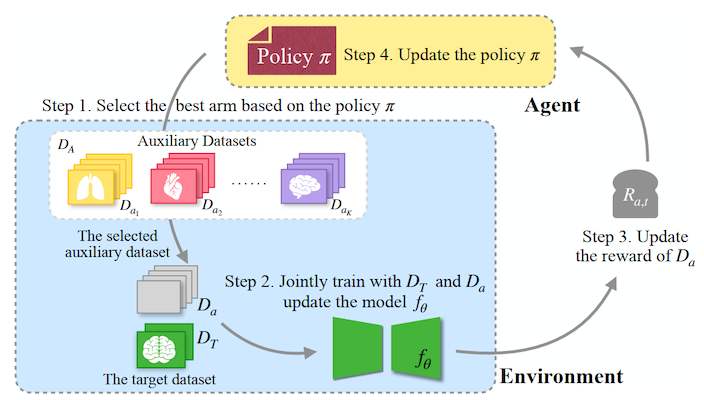
Adapting Foundation Models for Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation: Actively and Sequentially (ISBI’25)
A reliable and robust model adaptation framework for few-shot domain adaptation (FSDA) of medical image processing tasks. It formulates FSDA as a multi-armed bandit problem that actively selects auxiliary datasets to jointly train with the target task. (more info)
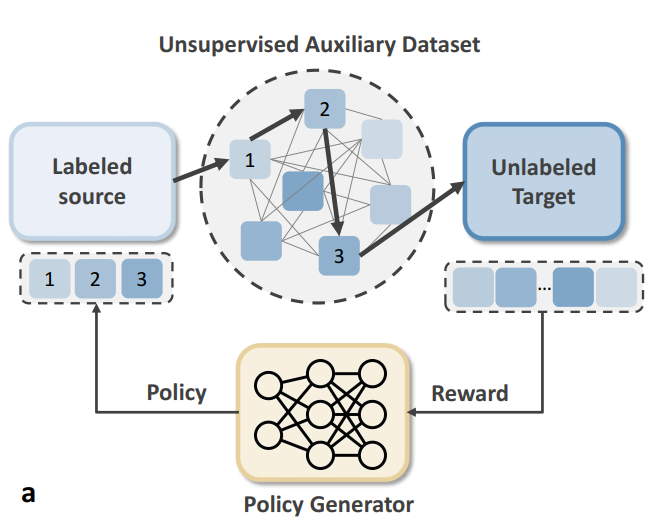
Reinforced Domain Selection for Continuous Domain Adaptation (ICASSP’25)
A key challenge in continuous domain adaptation is how to select the optimal sequence of intermediate domains that achieve the best adaptation performance on the target domain. We propose an unsupervised continuous domain adaptation framework that uses reinforcement learning to learn the optimal intermediate domain selection policy for a given target domain. (more info)
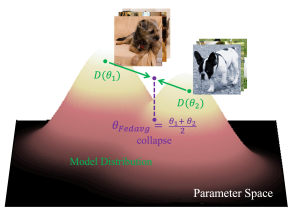
pFedGPA: Diffusion-based generative parameter aggregation for personalized federated learning (AAAI’24)
Traditional federated learning methods rely on linear parameter aggregation, which overlooks the complex structures of the parameter space, especially when client data have large distribution shifts. We propose pFedGPA, a generative parameter aggregation framework based on diffusion model for personalized federated learning. (more info)
Generalizing to Unseen Domains with Wasserstein Distributional Robustness under Limited Source Knowledge (IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process, 2024), (ICLR Workshop 2021)
Domain generalization aims at learning a domain-agnostic model from multiple source domains for any unseen target domain in the future. In this work, we solve the domain generalization problem using the concept of Wasserstein distributional robust optimization. (more info)
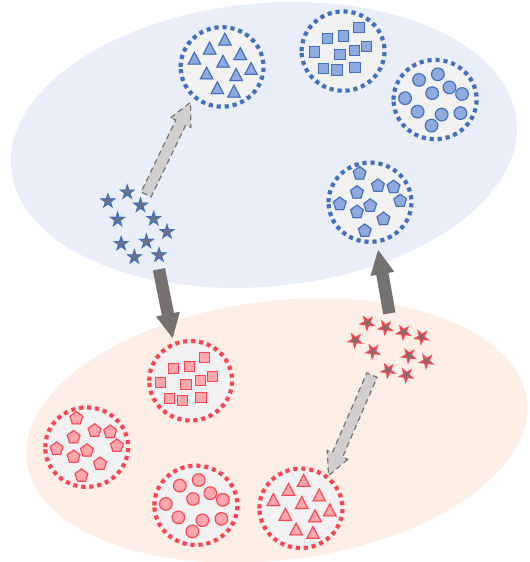
Enhancing Continuous Domain Adaptation with Multi-Path Transfer Curriculum (ACM PAKDD’24)
A continuous domain adaptation model, W-MPOT, which adapts source domain training data to distant target domain with the help of intermediate domains. It finds an optimal ‘‘transfer curriculum’’ of intermediate domains and regularizes the optimal-transport based continous adaptation with novel multi-path constraints. (more info)
Few-Shot Cross Domain Battery Capacity Estimation (ACM Ubicomp’21)
In data-driven battery capacity estimation, different battery sizes, testing environments and historical load patterns cause large domain shifts between training and testing data. We propose an optimal transport based domain adaptation method that is both efficient and accurate for few-shot cross-domain capacity estimation. (more info)
Multi-task and multi-modal learning
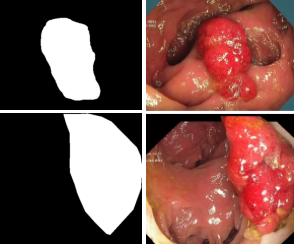
CCIS-Diff: a Generative Model With Stable Diffusion Prior for Controlled Colonoscopy Image Synthesis (ISBI’25)
A controlled generative model for high-quality Colonoscopy Image Synthesis based on a Diffusion architecture. It offers precise control over both the spatial attributes and clinical characteristics of polyps that align with clinical descriptions.
Flemme: A Flexible and Modular Learning Platform for Medical Images (BIBM’24)
A FLExible and Modular deep learning platform for MEdical images. Also featuring a multi-modal fusion scheme that incorporates a pyramid loss to optimize and fuse vertical features from different modalities. (more info)
Joint PVL segmenation and hand function classification (MICCAI’21)
A semi-supervised multitask learning framework to jointly learn PVL lesion segmentation and manual ability classification for MRI scans. Two clinically related auxiliary tasks are incorporated to improve the classification accuracy while requiring only a small amount of manual annotations. (more info)
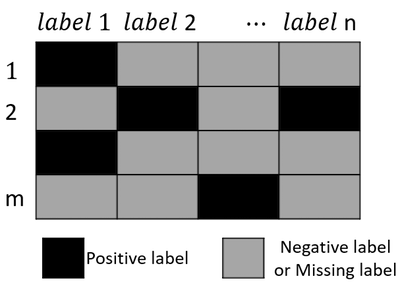
Maximal correlation embedding network for multilabel learning with missing labels (IEEE ICME’19)
Missing label is a common problem in real world multi-label learning datasets, where some of the labels associated with a sample may be missing due to sensor or human annotation error. We propose a robust maximal correlation embedding network for multi-label classification with missing labels. It has been successfully applied to multimedia and human context recognition data. (more info)
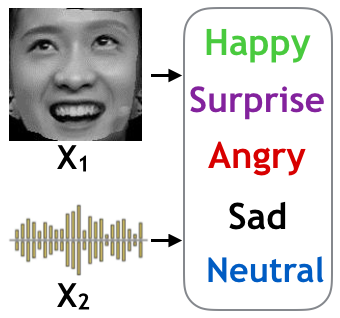
Multimodal emotion recognition: extracting public and private information (IEEE ICME ’19)
An end-to-end emotion recognition framework using both visual and audio input. It learns a multi-modal representation that captures both dependences between different input modalities, and modal-dependent information in each modality. (more info)
Topological data analysis
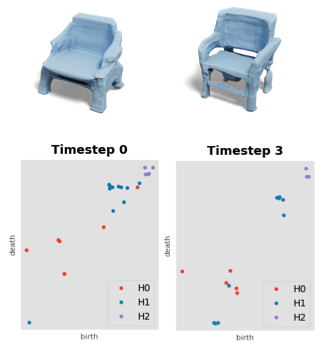
Enhancing Implicit Shape Generators Using Topological Regularizations (ICML’24)
A principled approach that utilizes topological regularization losses on an implicit shape generator. By aligning the persistent diagram distributional of generated shapes and training shapes, and enforcing the local smoothness of PDs, we significanly improved the topological quality of synthetic shapes. (more info)
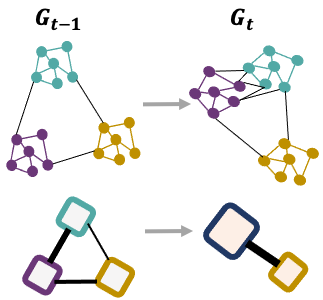
Learning Persistent Community Structures in Dynamic Networks via Topological Data Analysis. (AAAI’24)
A novel deep graph clustering framework with temporal consistency regularization on inter-community struc- tures, inspired by the concept of minimal network topolog- ical changes within short intervals. (more info)
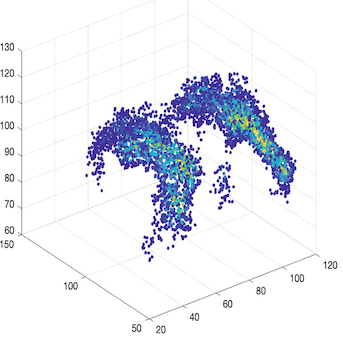
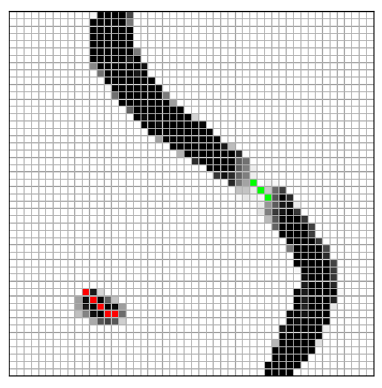
Topology-Preserving Hard Pixel Mining for Tubular Structure Segmentation (BMVC’23)
A skeleton-based hard pixel mining strategy for training end-to-end segmentation networks for tubular structures, penalizing topology-relevant yet mis-segmented pixels in overall cost function. Skeletal hard pixels are mined through several simple logical and morphological operations which are fast and scalable. (more info)
Mobility data analysis
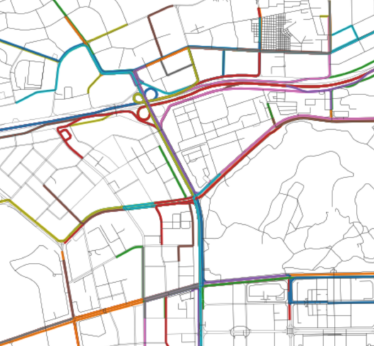
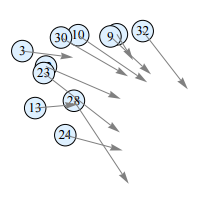
Explainable Trajectory Representation through Dictionary Learning (ACM SigSpatial’23)
A dictionary learning approach for encoding trajectories on a network in an explainable and efficient way. It learns a set of frequently traversed path segments (pathlets) that optimally reconstruct every trajectory by concatenation. The resulting representation is naturally sparse and encodes strong spatial semantics. (more info)
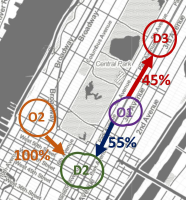
Urban mobility pattern mining based on regional dependencies (EAI MobiQuitous’18) (Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020)
A novel mobility pattern mining algorithm that learns the dynamics between different spatial regions from taxi trip data. It proposes kernelized ACE, which efficiently finds latent embeddings for trip origins and destinations while maintaining the correlation between them. The resulting embedding can be used to extract strong mobility patterns while partitioning the city into non-overlapping regions at the same time. (more info)
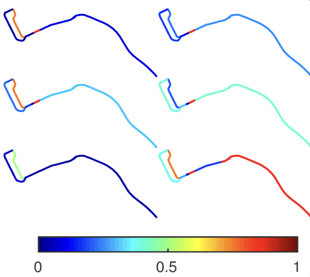
Travel time prediction from limited GPS floating cars (ACM SigSpatial’17), (ACM Trans. Spat. Algorithms Syst. 2019)
A trajectory-based travel time prediction algorithm when only a small number of GPS floating cars are available. It learns the travel time patterns of a compact set of frequently shared paths from historical data. Given a travel time prediction query, we identify the current travel time pattern from recent trajectories, then infer its travel time in the near future. (more info)
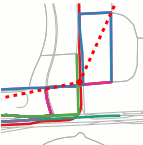
Knowledge-based trajectory completion (ACM SigSpatial’16)
A framework to "densify" sparse GPS trajectories without relying on the roadmap data. We are able to recover geometric details of complex junctions, and improve the accuracy of real life traffic trajectories. (more info)
Data-driven map matching (ACM SigSpatial’13)
A robust multitrack map matching algorithm for sparse and noisy GPS trajectories. It simultaneously learns the regular structures in taxi trajectories and map match all trajectories simultaneously. (more info)
Mining leader-follower realtionships from GPS trajectories (CG:YRF’12 Workshop)
A case study on understanding the leader-follower phenomenum in the group movement of cows from their trajectories. We use geometric and correlation based constraint to extract leader-follower relationships. (more info)
Social data mining
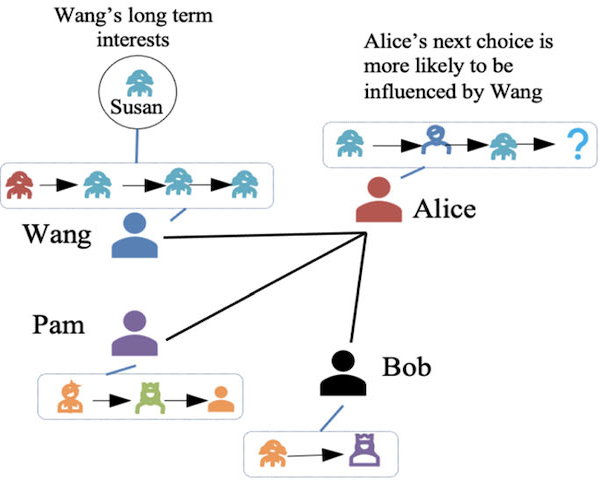
Session-based recommendation with temporal dynamics (2023)
A session-based recommendation framework for large volunteer networks that employs temporal dynamics to capture uncertainty caused by the changing structure of volunteers’ participation behaviour. (more info)
Optimising Self-organized Volunteer Behaviors during COVID-19 Pandemic (2022)
A quantitive study on how volunteers collaborate to achieve rapid mobilisation during the COVID-19 outbreak, using the concept of self-organisation. It proposes a data-driven framework to investigate when and how self-organisation emerged during the pandemic response and how it relates to effectiveness of volunteer organisations in general. (more info)