A Transferability-Based Method for Evaluating Protein Representations
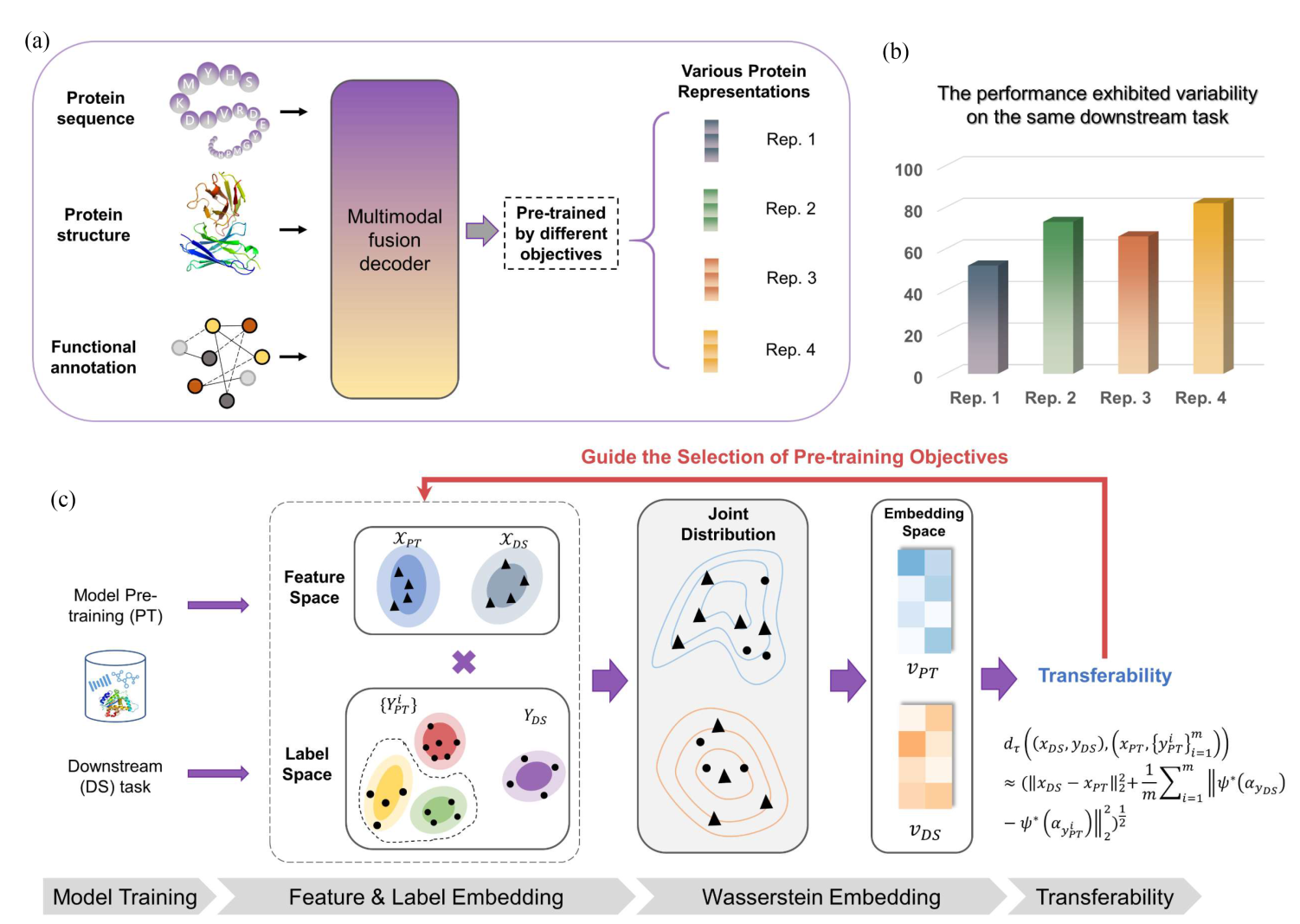
Quantitative selection of the optimal pre-training model for downstream biological tasks. (a) multi-modal protein data trained with multiple objectives, yielding a variety of pre-trained protein representations. (b) Performance variation of these different pre-trained protein representations on the same downstream task. (c) The proposed method for quantifying the transferability from a pre-trained protein representation to downstream tasks, which can help selecting pre-training objectives.
Self-supervised pre-trained language models have recently emerged as a powerful approach in learning protein representations, showing exceptional effectiveness in various biological tasks, such as drug discovery. Amidst the evolving trend in protein language model development, there is an observable shift towards employing large-scale multimodal and multitask models. However, the predominant reliance on empirical assessments using specific benchmark datasets for evaluating these models raises concerns about the comprehensiveness and efficiency of current evaluation methods.
Addressing this gap, our study introduces a novel quantitative approach for estimating the performance of transferring multi-task pre-trained protein representations to downstream tasks. This transferabilitybased method is designed to quantify the similarities in latent space distributions between pre-trained features and those fine-tuned for downstream tasks. It encompasses a broad spectrum, covering multiple domains and a variety of heterogeneous tasks.
To validate this method, we constructed a diverse set of protein-specific pre-training tasks. The resulting protein representations were then evaluated across several downstream biological tasks. Our experimental results demonstrate a robust correlation between the transferability scores obtained using our method and the actual transfer performance observed. This significant correlation highlights the potential of our method as a more comprehensive and efficient tool for evaluating protein representation learning.
Publication
| Self-supervised pre-trained language modelshave recently attracted huge attention as a powerful approach in learning protein representations, showing exceptional effectiveness invarious biological tasks, such as drug discovery. | ppt |
@article{hu2024transferability,
title={A Transferability-Based Method for Evaluating the Protein Representation Learning},
author={Hu, Fan and Zhang, Weihong and Huang, Huazhen and Li, Wang and Li, Yang and Yin, Peng},
journal={IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics},
year={2024},
publisher={IEEE}
}
