Dataset & Project Ideas
Below are some potential datasets and topics for your class project. Please contact the course staff if you have questions about these datasets.
 |
1. Planning and Behavior Synthesis with Generative ModelsLeverage generative models (e.g., diffusion models) for planning in imitation learning or multi-agent systems. Project ideas:
Reference papers:
|
 |
2. AI for Construction Site Safety MonitoringBy combining machine learning techniques with construction site safety, we can create systems that not only predict and prevent accidents but also automate and optimize safety measures in real-time. Project ideas:
Reference papers:
Related Datasets:
|
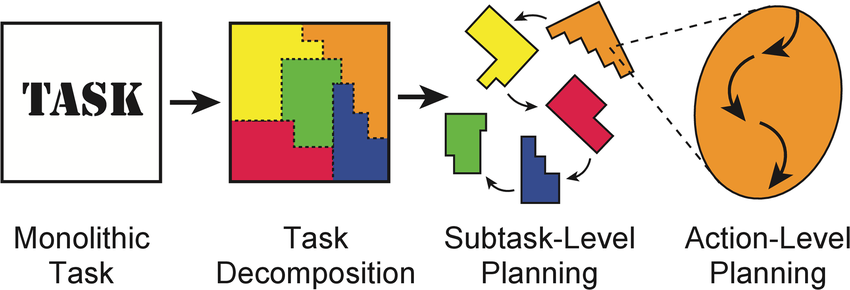 |
3. Task compositionallyHow to breakdown complex tasks into simpler component tasks and combining them to form solution? This question can be studied in both the supervised learning (e.g. question answering, visual perception), unsupervised learning (e.g. generative model) and reinforcement learning (e.g. skill planning) scenarios. How to decompose multimodal tasks? One can also take a theoretical perspective to investigate when composed model can have better performance than a single model. Reference papers:
|
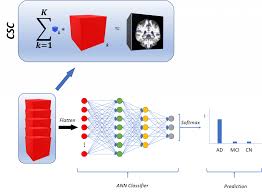 |
4. Sparse Coding in Neural Networks:Investigate how integrating sparse coding principles into neural network architectures can improve model interpretability and efficiency, particularly in resource-constrained environments. Reference papers:
|
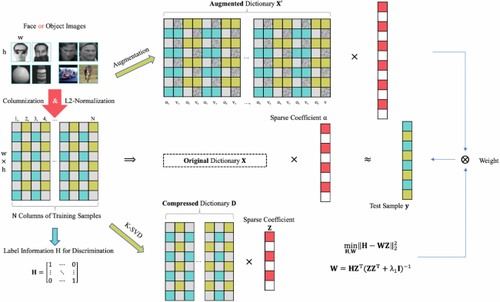 |
5. Robust Dictionary Learning under NoiseInvestigate methods to enhance the robustness of dictionary learning algorithms in the presence of noise and outliers, with applications in audio and image processing. Reference paper:
|
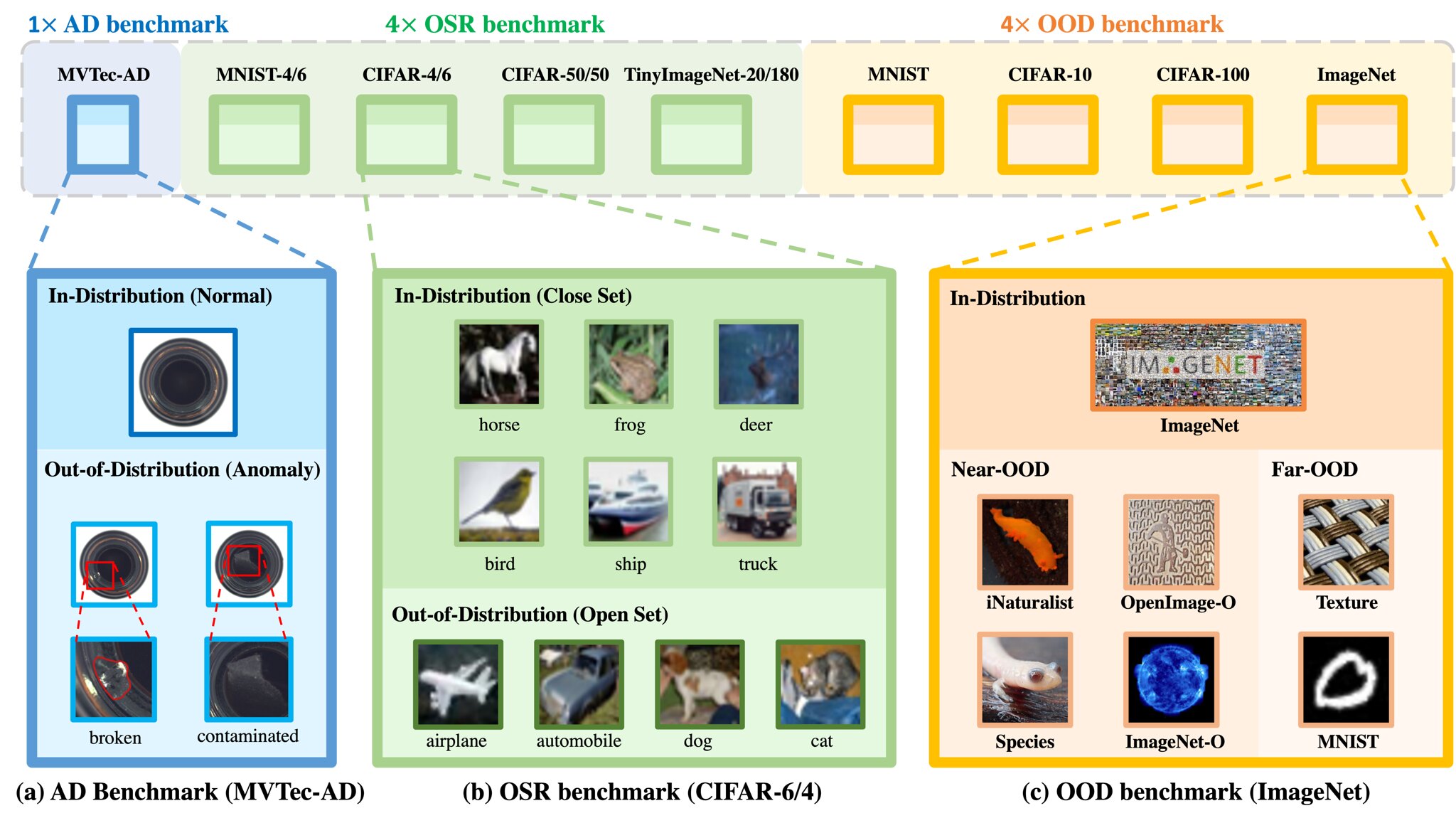 |
6. Out-of-distribution DetectionCurrent NNs can give likelihood and probability for known classes. When a new class or different style emerge, they may not perform well. Investigate and Design a framework to detect new unseen classes. Reference paper:
|
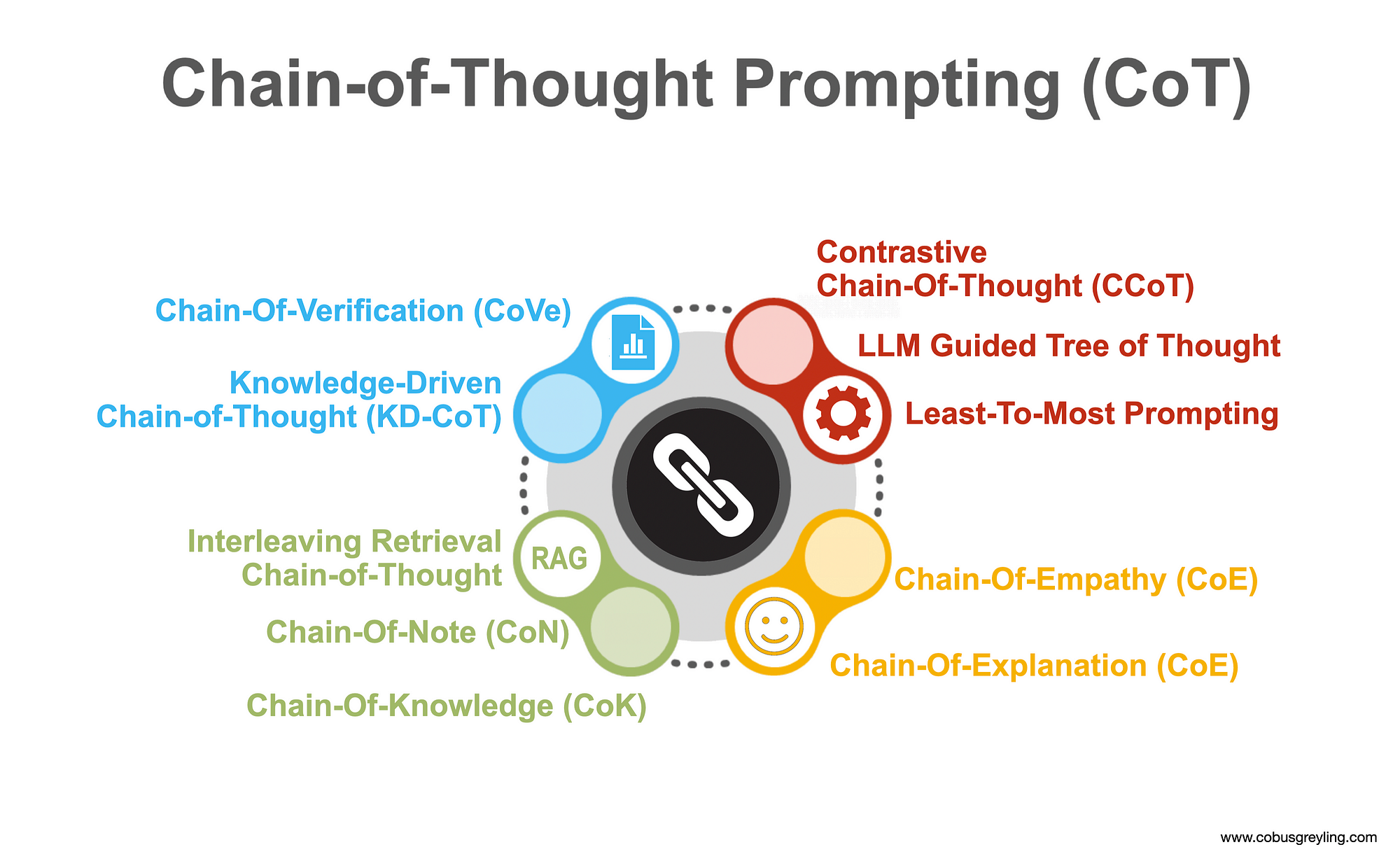 |
7. Stable Chain-of-thoughtChain-of-thought has been developed in LLM systems recently. However, how to improve its stability and effectiveness in diverse tasks remain a challenge. Try to combine the methods you have learnt to improve it. Reference paper:
|
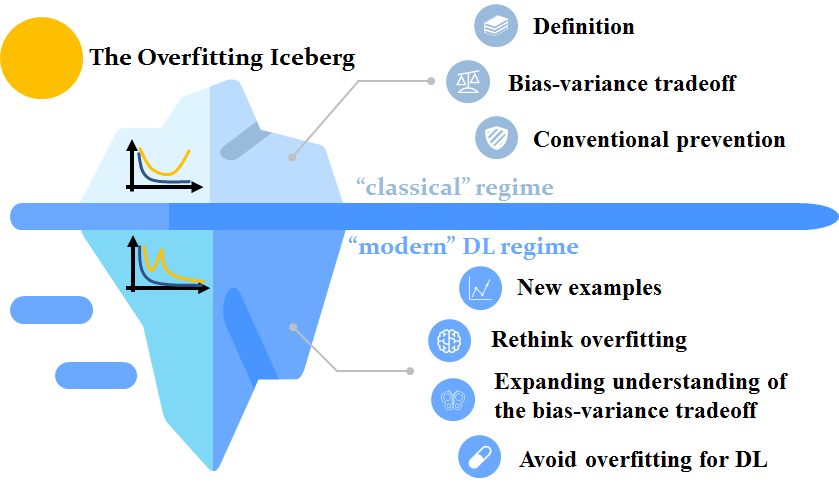 |
8. Multiple descent behavior in machine learningAnalyze the condition of multiple descent behavior in context other than supervised learning (e.g. unsupervised learning, graph learning, etc). Reference paper:
|
